This is the equation employed in the spreadsheet.
- ΔP is the pressure loss in the pipe (Pa)
- ρ is the liquid density (kg m-3)
- μ is the liquid viscosity (Pa s)
- g is the gravitational constant (9.81 m s-2)
- L is the length of the pipe (m)
- D is the pipe diameter (m)
- V is the liquid velocity (m s-1)
- f is the Darcy Fanning friction factor
The calculation is iterative, and requires the use of Excel's Goal Seek. However, this is automated in the spreadsheet so you only have to click a button and some VBA initiates Goal Seek for you.
The Darcy-Weisbach equation should only be used for steady-state incompressible flow. It can also be used for open-channel flows by replacing the diameter with the 4 R, where R is the hydraulic diameter. The hydraulic diameter is simply the cross-sectional area divided by the wetted perimeter.
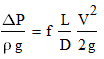

No comments:
Post a Comment